Heart Disease: A Silent Death
Hector Hernandez
Co-Presenters: Paolo Alvarado
College: The Dorothy and George Hennings College of Science, Mathematics and Technology
Major: Computer Science
Faculty Research Mentor: Ching-yu Huang
Abstract:
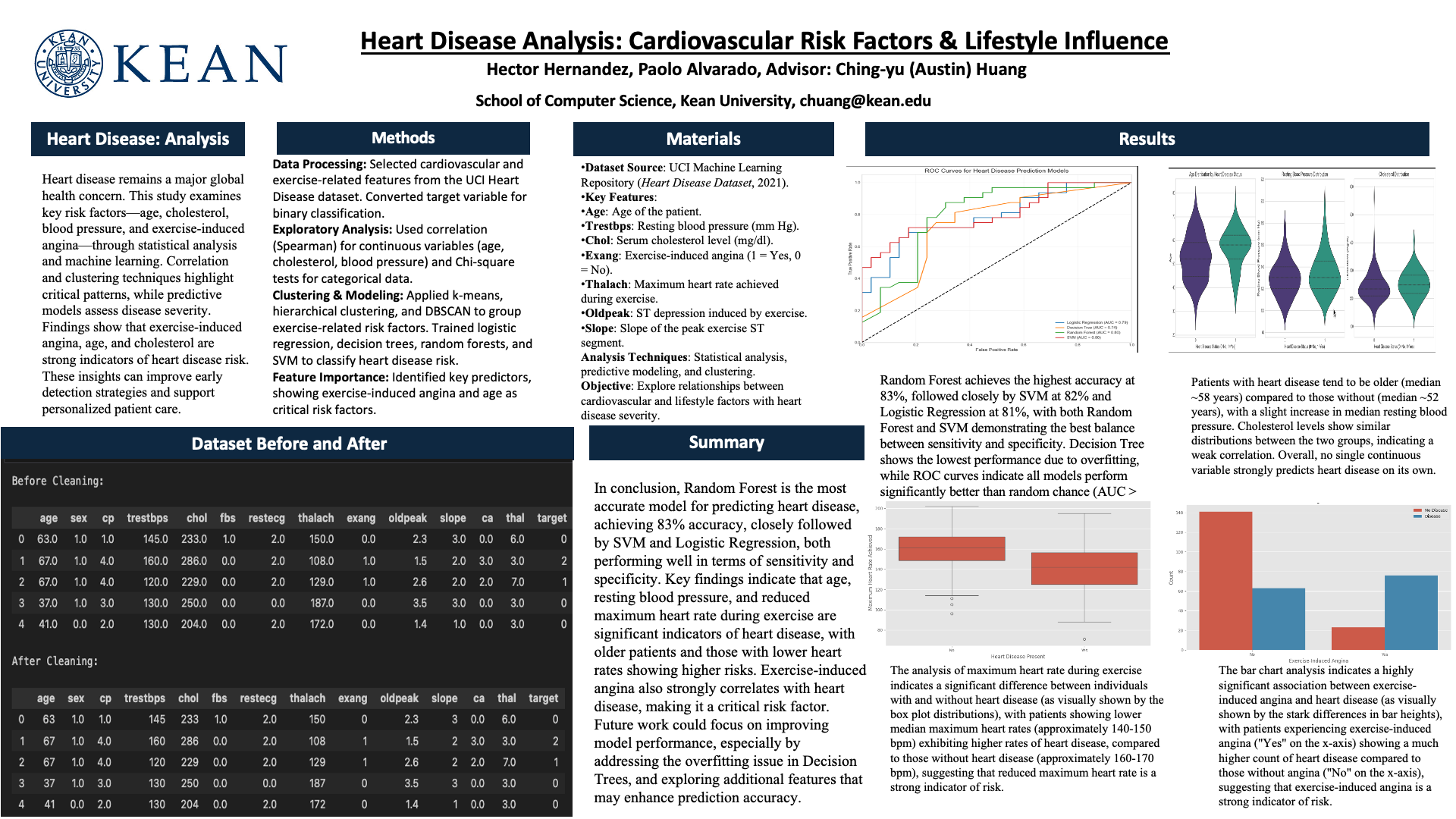
Both biological and behavioral factors contribute significantly to the prevalence and severity of heart disease, which remains a major global health concern. The purpose of this study is to look into two important aspects of heart disease risk: lifestyle factors, exercise, and cardiovascular factors. Person 1 employs statistical analysis and predictive modeling methods such as logistic regression to examine the association between the severity of heart disease and the three main cardiovascular risk indicators: age, resting blood pressure (trestbps), and cholesterol levels (chol). With a focus on clustering and visualizing the effects of exercise on heart disease, Person 2 investigates the impact of exercise on heart health by examining characteristics like maximum heart rate (thalach), exercise-induced angina (exang), ST depression during exercise (oldpeak), and the slope of the ST segment (slope).By comparing findings from both analyses, this study seeks to identify dominant risk factors and provide actionable insights for healthcare professionals, improving early detection, risk assessment, and patient management strategies for cardiovascular conditions.