Utilization of Mirror Therapy to Reduce Quadriceps Lag Post Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report
Seaerra Michalsky
Co-Presenters: Caitlin Boyko, Thomas Koc, Claire Murphy
College: The College of Health Professions and Human Services
Major: Physical Therapy (DPT)
Faculty Research Mentor: Caitlin Boyko
Abstract:
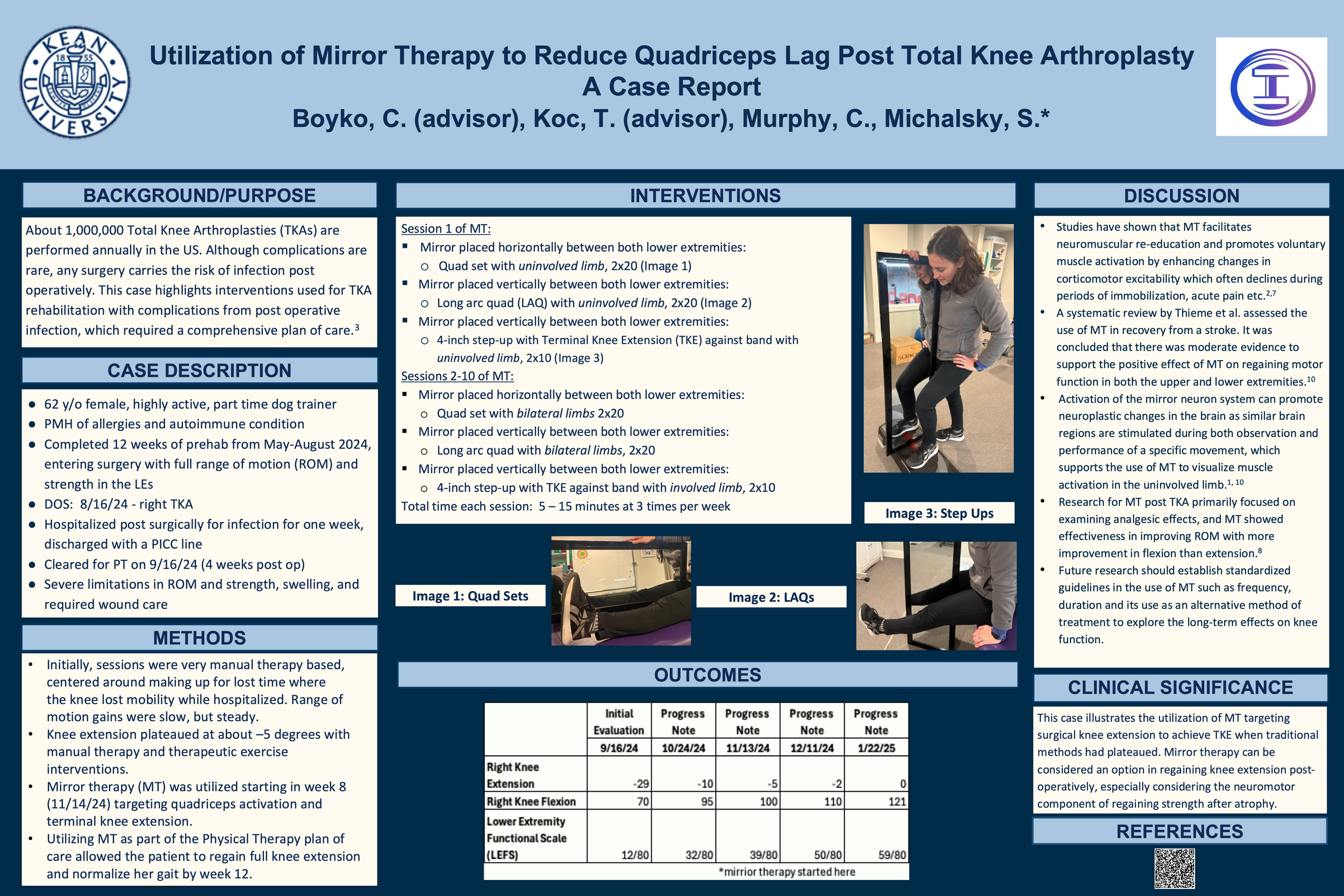
Title: Utilization of Mirror Therapy to Reduce Quadriceps Lag Post Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case ReportAuthors: Boyko, C., Koc, T., Murphy, C., Michalsky, S., Department of Physical Therapy, Kean UniversityAbstract:Mirror therapy is an intervention that first emerged as a rehabilitative technique to produce an analgesic effect for amputees and has since expanded in use to address various neurological deficits. A mirror is placed blocking vision of a patient’s affected limb, so the patient sees a mirror image of the unaffected extremity instead, which can drive neurological adaptations in the involved extremity. This case report illustrates the physical therapy interventions and outcomes of a 62-year-old highly active female who underwent a total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The patient completed twelve weeks of prehabilitation prior to her surgical date, entering surgery with full range of motion (ROM) and strength in her lower extremities. However, a post-operative infection developed which required hospitalization for one week. She was later discharged with a PICC line for antibiotics, and cleared to start physical therapy (PT) after four weeks. The patient presented to PT with severe limitations in her surgical knee ROM and strength, increased edema, and required routine wound care. Initially, treatment was heavily based on manual therapy to reestablish ROM. Over time, the gains made in ROM with traditional interventions such as manual therapy and therapeutic exercises plateaued lacking about 5 degrees of knee extension, inhibiting normal gait pattern. At this time, mirror therapy for knee extension through quadriceps activation was introduced. Although mirror therapy is not commonly utilized in orthopedic cases, the patient was able to regain terminal knee extension and ambulate without restriction. This case illustrates the importance of considering and implementing a complementary therapy technique such as Mirror Therapy to target post-surgical terminal knee extension ROM deficits for TKA rehabilitation when other standard plans of care have plateaued.Keywords: Mirror Therapy, Total Knee Arthroplasty, Neuroplasticity, Complementary Therapy